from Terry Hayek
As a continuation of ours 9 Characteristics of 21st Century Learning developed in 2009, we developed an updated framework, The inside-out learning model.
The goal of the model is simple enough – not purely academic mastery, but instead authentic self-knowledge, diverse local and global interdependence, adaptive critical thinking, and adaptive media literacy.
By design, this model emphasizes the role of play, diverse digital and physical media, and the designed interdependence between communities and schools.
The attempt to personalize learning takes place through new drivers and new notions of local and global citizenship. Ann School from the inside out brings learners, learning and ‘accountability’ back out of academia and back into communities. It is no longer taught in schools. Rather, they act as curators of learning resources and tools and encourage shifting the ‘burden’ of learning back to a more balanced perspective of stakeholders and participants.
Here, families, business leaders, humanitarian organizations, neighbors, mentors, and institutions of higher learning come together to witness, honor, respond, and support the learning of members of their own community.
The micro-effect here is increased intellectual intimacy, while the macro-effect is healthier communities and citizenship that extends beyond mere participation to ideas of thinking, scale, legacy and growth.
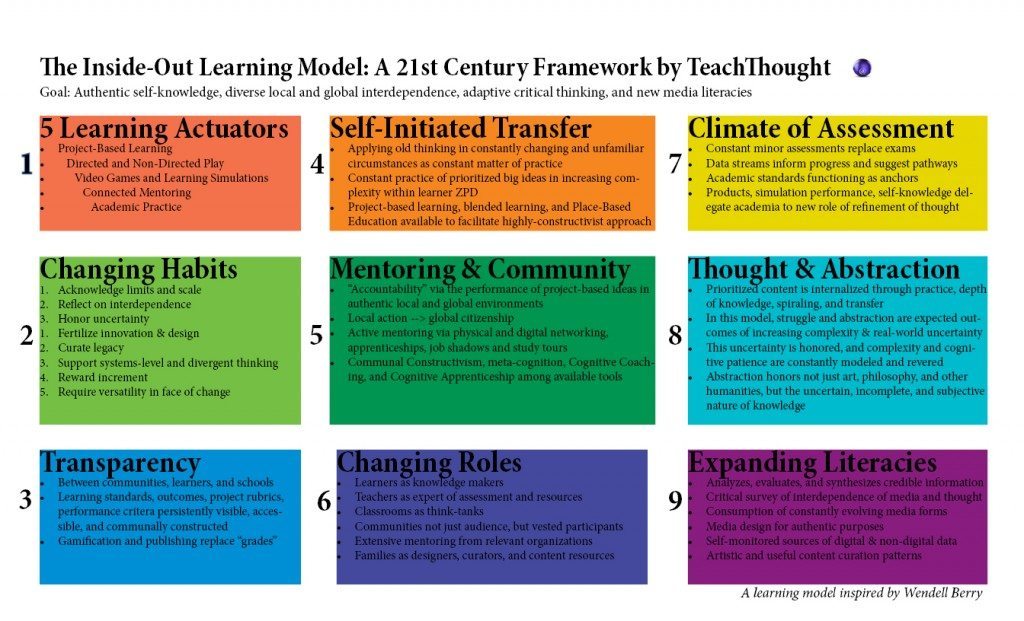

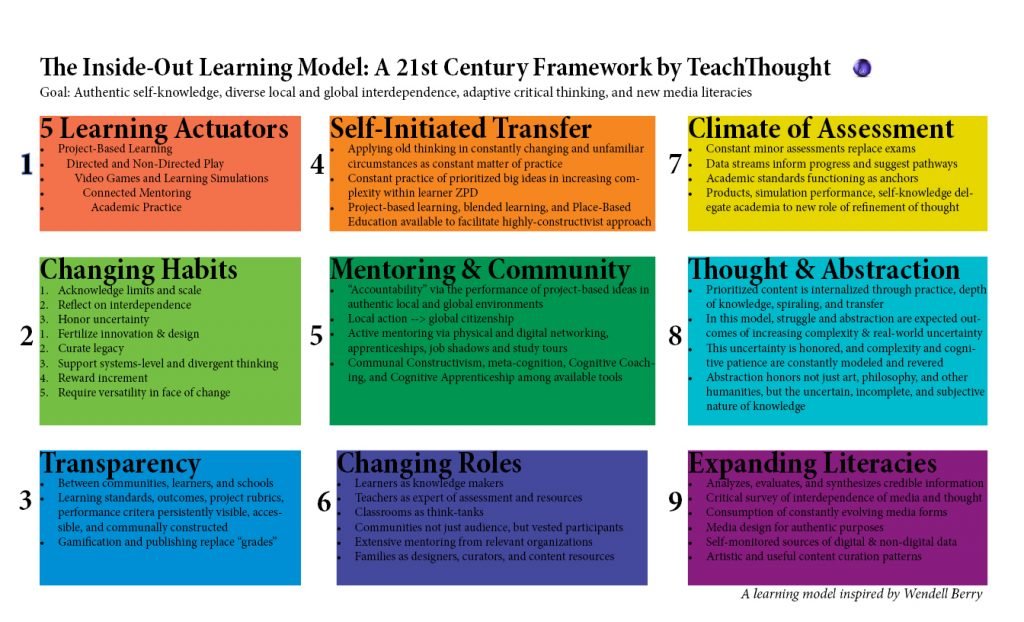
The 9 domains of the inside-out learning model
1. Five learnable actuators
- Project-based learning
- Directed and undirected play
- Video games and learning simulations
- Related Mentoring
- Academic practice
2. Changing habits
- Well-being (for teachers and students) as an issue worthy of innovation and design
- Confirm the boundaries and scale
- Think about interdependence
- Honor the uncertainty
- Maintain the legacy
- Maintain systems level and divergent thinking
- Reward increase
- Require flexibility in the face of change
3. Transparency
- Between communities, learners and schools
- Learning standards, outcomes, project rubrics, performance criteria permanently visible, accessible and built by the community
- Gamification and publishing replace ‘ratings’
4. Self-initiated transfer
- Applying old thinking to ever-changing and unfamiliar circumstances as a constant practice
- Consistent practice of prioritized big ideas of increasing complexity within the learner’s Zone of Proximal Development
- Project-based learning, blended learning and place-based learning available to facilitate a highly constructivist approach
5. Mentoring and community
- “Accountability” by presenting project-based ideas in authentic local and global environments
- Local action –> global citizenship
- Active mentoring through physical and digital networks, apprenticeships, job shadowing and study trips
- Communal constructivism, meta-cognition, cognitive coaching and cognitive apprenticeship among the available tools
6. Reversal of roles
- Learners as creators of knowledge
- Teachers as assessment and resource experts
- Classrooms as think tanks
- Communities are not only audiences but also empowered participants
- Families as designers, curators, and content resources
7. Evaluation climate
- Permanent minor grades replace exams
- Data streams inform progress and suggest pathways
- Prioritized and anchored academic standards
- Products, simulation, self-awareness are delegating academia to a new role of advancing thought
8. Thought and abstraction
- In this model, struggle and abstraction are expected outcomes of increasing complexity and uncertainty in the real world
- This uncertainty is honored, and complexity and cognitive patience are constantly modeled and honored
- Abstraction honors not only art, philosophy, and other humanities, but also the uncertain, incomplete, and subjective nature of knowledge
9. Expanding literacy
- Analyzes, evaluates and synthesizes reliable information
- A critical review of the interdependence of media and thought
- Consumption of ever-evolving media forms
- Media design for authentic purposes
- Self-observed digital and non-digital data sources
- Artistic and useful content curation models
The Inside-Out Model of Learning Central Theories and Learning Artifacts: Situational Learning Theory (Leve), Discovery Learning (Brunner), Communal Constructivism (Holmes), Zone of Proximal Development and Better Known Other (Vygotsky), Learning Cycle ( Kolb), Transfer (Thorndike, Perkins, Wiggins), Mental Habits (Costa and Kalik), Paulo Freire and all of Wendell’s work Berry