from Staff
We are interested in TeachTought supporters of all learning taxonomies.
(We even created our own, Teachthorge Texming Taxonomy.)
Learning taxonomies helps us think how training is happening, emphasizing that there are many ways to frame our thinking.
Bloom’s digital taxonomy adapts the original Bloom cognitive framework for digital learning, helping the K-12 teachers integrate technology while building basic thinking skills. Taxonomy organizes digital actions in levels such as remembering, understanding, applying, analysis, evaluation and creation, each with verbs based on technologies that maintain specific teaching goals.
This means that we can have taxonomies for differentiation and taxonomies for thinking and taxonomies for tasks and evaluation – so many opportunities to explore the actual process of thinking, learning and applying everyone.
This leads to cool visualizations –Bloom’s taxonomic postersFor example.
It can also lead to tools that help design lessons, units and evaluations –Bloom’s taxonomic verbs Work well here.
You can get a Ready for the class version Bloom’s digital taxonomy for $ 6.95.
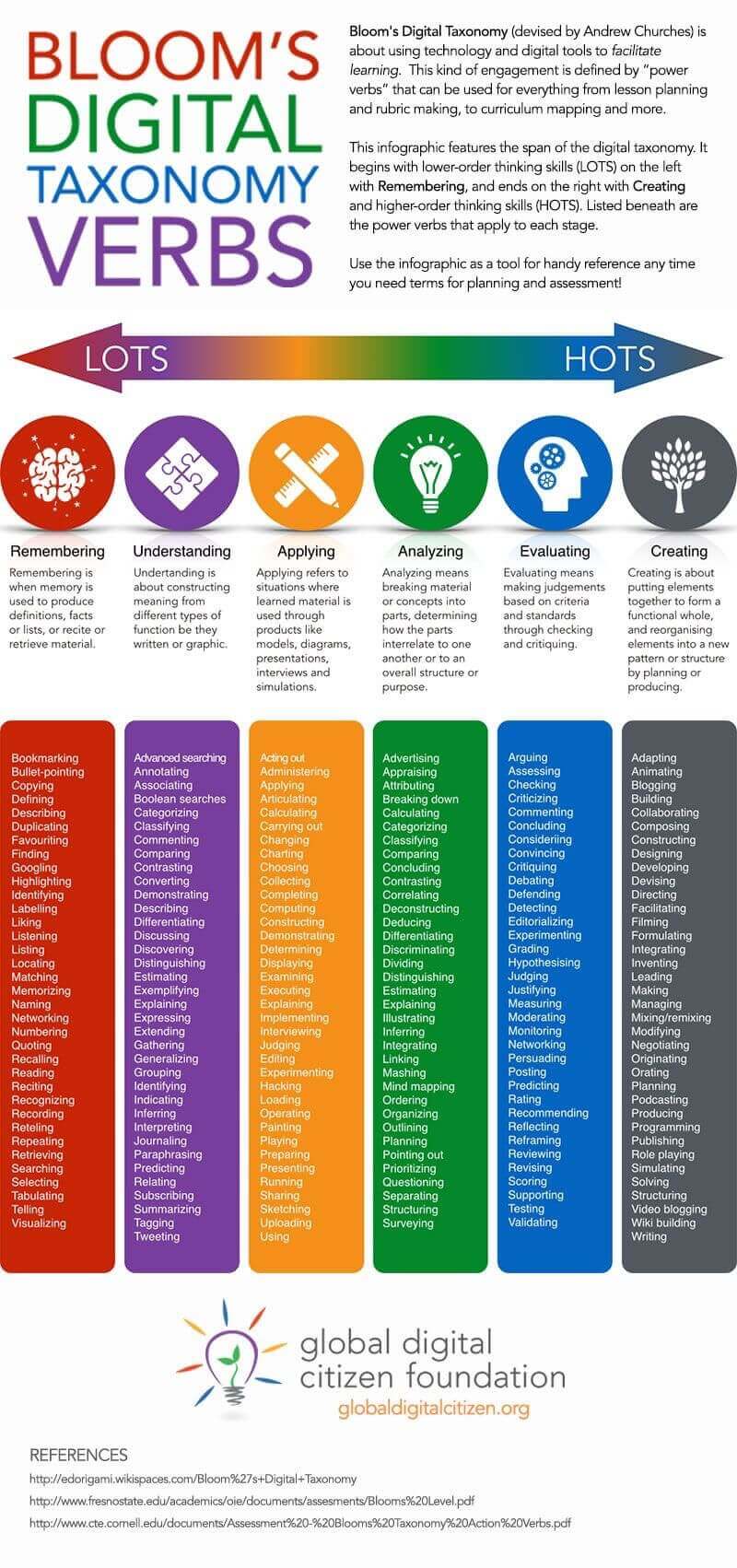
This type of Bloom taxonomy with digital and social instruments – can help teachers make a more intentional choice of how students engage in content in the modern learning environment. In the graphics, we have organized 126 “Power Verbs”, which are usually related to digital learning at known levels of Bloom’s: Remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate and create. You will see verbs as moderate, duplicated, blog, build Wiki, and podcast– All examples of how technology can shape and expand students’ thinking.
However, it is important to understand that these categories are not firm. One verb can appear on several levels depending on the context. BlogsFor example, it may include a simple recall in one assignment and synthesis in a higher order or evaluation in another. This flexibility is part of what makes the Bloom taxonomy useful – but also why it is never a perfect fit.
After all, the value is not to obtain every verb in the right place. The value is to think carefully about the types of thinking that we ask students to do – and how digital instruments can deepen or extend this thinking in meaningful ways. Whether you use this exact framework or not, the exercise of connecting cognitive processes to digital tasks is a powerful way to sharpen your planning and better support critical thinking in your classroom.
The result is an instrument that can help teachers think about higher-order thinking levels that enter these types of activities and projects. To be clear, just because the verb is in one category does not mean that it cannot be used at higher or higher levels of thinking (ie to appear in other categories Bloom’s digital taxonomy).
Looking for a traditional version of Bloom verbs? See our Bloom’s taxonomic verbs for teaching and planningS
Do you want to see how these verbs are visually aligned with the levels of thinking? Look at ours Bloom’s digital taxonomyS
In fact, there is a significant amount of subjectivity and editing that enters any framework, which suggests that it outlines how thinking happens. This is not an accurate science. Nevertheless, just the fact that we explore thinking and digital tasks and students together is at least as valuable as any framework by itself.
By doing this type of work, we collectively – you, learning, administrators, schools, researchers, universities, etc. – We can develop “proficiency” in the gloomy and abstract area of applied neurology. We can begin to understand how understanding is.
Bloom Gerbs digital taxonomy
We hope that the graphics are useful for research, discuss, planning and otherwise participate in Bloom’s digital taxonomy.
You can also find a classroom ready for a version of our Bloom taxonomy taxonomy digital planning verbs and cards Shorten preparation time and focus on wider strategies for planning lessons and units for your students.
If you have verbs you want to see added to the diagram, let us know in the comments below.
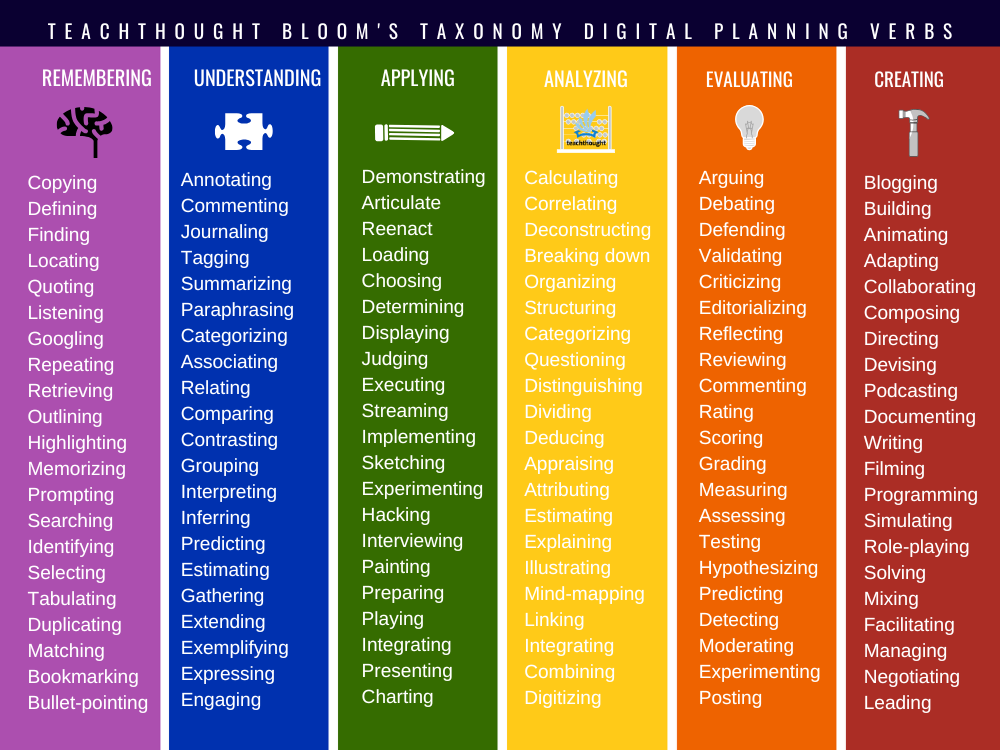
126 Bloom Taxonomic Verbs for Digital Training
Memorial
- Copying
- Determination
- Finding
- Location
- Quotation
- Listening
- Googling
- Repetition
- Retrieval
- Delineation
- Highlight
- Storage
- Prompt (Chatgpt, for example)
- Search
- Identification
- Choice
- Tabulation
- Duplication
- Coincidence
- Bookmarks
- Bullet points
Understanding
- Annotation
- Comment
- Magazines
- Marking
- Summarization
- Paraphrase
- Categorization
- Association
- Relationship
- Comparison
- Contrasting
- Grouping
- Interpretation
- Conclusion
- Prediction
- Evaluation
- Gathering
- Extension
- Example
- Expression
- Engagement
Implementation
- Demonstration
- Articulated
- Recovery
- Charging
- Choice
- Determination
- Display
- Refereeing
- Implementation
- Streaming
- Implementation
- Sketching
- Experimentation
- Hack
- Interview
- Picture
- Preparation
- Play
- Integration
- Presentation
- Diagram
Analysis
- Calculation
- Correlation
- Deconstruction
- Smashing
- Organization
- Structuring
- Categorization
- Interrogation
- Distinction
- Division
- Alignment
- Evaluation
- Attribution
- Evaluation
- Explanation
- Illustration
- Mapping
- Connection
- Integration
- Combination
- Digitalization
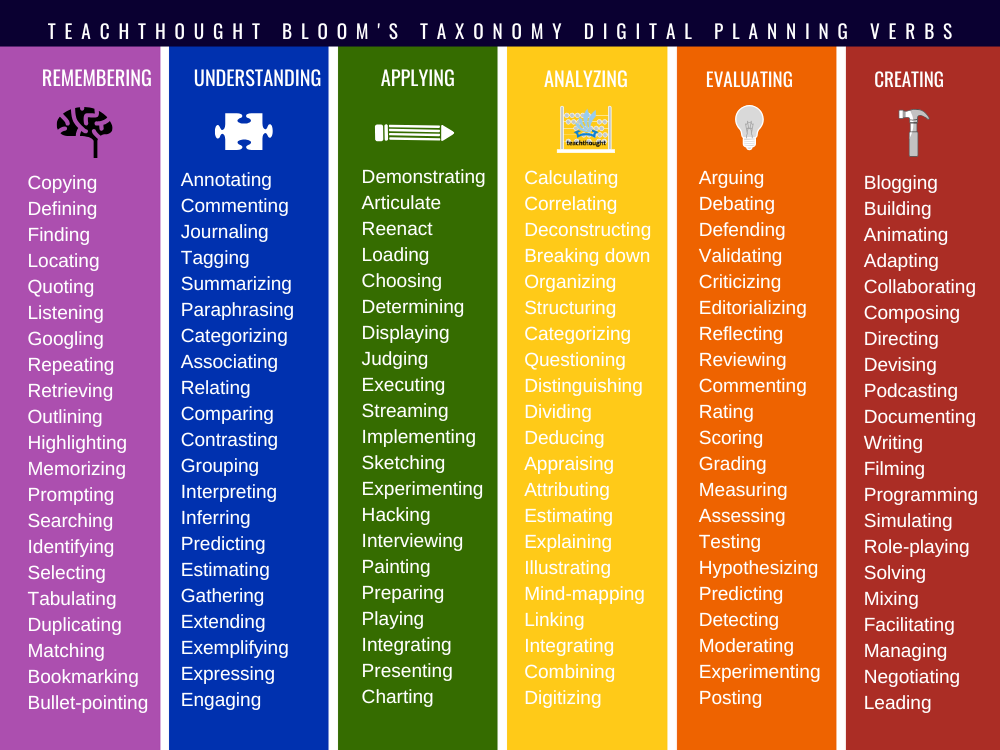
Evaluation
- Argumentation
- Debate
- Protection
- Validation
- Criticism
- Editorial
- Reflective
- Review
- Comment
- Evaluation
- Scoring
- Evaluation
- Measurement
- Evaluation
- Testing
- Hypothetic
- Prediction
- Detection
- Moderation
- Experimentation
- Publication
Creation
- Blogs
- Building
- Animation
- Adaptation
- Cooperation
- Composition
- Directing
- Streaming
- Subcastation
- Documentation
- Writing
- Capture
- Programming
- Simulation
- Role -play
- Resolution
- Mixing
- Facilitation
- Management
- Negotiations
- Leading
Another version of the Global Digital Citizen graphics appears below.