from Staff
Self -tuition It is not a new concept, but it is often misunderstood-especially in the context of K-12 classrooms.
In advance reflection, Terry Hayk explores the connection between self -assembled learning and the true purpose of education:
“The purpose of the model is not the knowledge of content (though it should lead to this), but more recently something closer to wisdom -training how to learn, understanding what is worth understanding, and perhaps the most important thing, analyzing the purpose of learning (such as personal and social change).
Self -assembled training acquires grip as teachers are looking to modernize teaching practices. With the increase in dissatisfaction with the traditional school and with the wealth of online resources available in InformationThis is a powerful frame to help learners flourish independently. This model, promoted by Gerald Grow, breaks the trip in Four stages of self -assembled training– Undering reflection of the gradual discharge of teachers from responsibility are already well aware well.
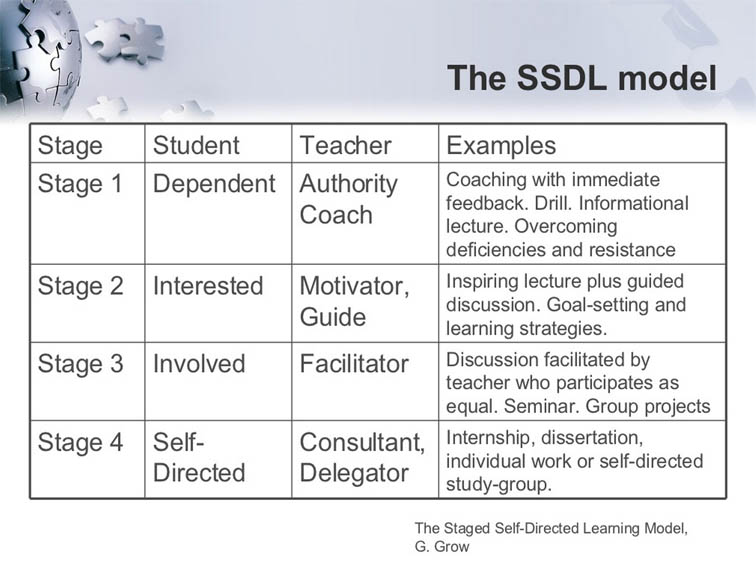

Stage 1: Dependent (teacher as authority and coach)
At this stage, students rely almost entirely on teachers to introduce knowledge, provide structure and guide their training. They lack confidence and skills to learn independently.
- The role of the teacher: Act as a coach and authority, offering clear instructions and immediate feedback to build fundamental skills.
- Practical strategies:
- Meet students with new ideas through direct training, managed practice and skeleton.
- Use adaptive platforms such as Khan academy For structured skills exercise.
- Create safe opportunities for students to take small risks without fear of failure.
Stage 2: Interested (teacher as a motivator and guide)
Students begin to demonstrate curiosity and begin to take the initiative, but still rely on the teacher for structure and encouragement.
- The role of the teacher: Motivate and guide students, encouraging engagement through real -world experience relationships.
- Practical strategies:
- Use real -world training based projects to make the content meaningful and inspire a request.
- Played tutorials with instruments such as Classcraft or Quizizz To maintain commitment.
- Include goals and self -government lessons, helping students explore their own interests in structured parameters.
Stage 3: Participates (teacher as a facilitator)
Here students take an active role in their own training. They can set goals, cooperate with peers and manage tasks with minimal supervision.
- The role of the teacher: Facilitate by being a guide to the removal, promoting activities guided by students, while offering support when needed.
- Practical strategies:
- Encourage the students managed by students through group projects or seminar -style discussions. Use tools like Google Workspace to support teamwork.
- Enter inquiries -based training, encouraging critical thinking while students use research to ask and answer their own questions.
- Provide the students with selection menus or flexible project frames while giving them autonomy while maintaining boundaries.
Stage 4: Self -tune (teacher as consultant and delegator)
Students are now taking full responsibility for their training, regardless of setting goals, tracking progress and searching for resources. Teachers go into a consulting role, offering feedback and maintenance only as requested.
- The role of the teacher: Act as a consultant or delegator, retreating aside to let the students take over property.
- Practical strategies:
- Assign passionate projects or independent research tasks to encourage autonomy.
- Use tools as Concept or reflective magazines for training to track goals and progress.
- Include partner network accountability where students share goals and provide feedback to each other.
The purpose of self -assembled training
The ultimate goal of self-study is not simply a mastery of content, but achieving something closer to wisdom– compensation how to learn and understand Why Learning issues. This model encourages students to explore the relationship between study and applications in the real world such as work, citizenship and personal growth.
With effective guidance through these four stages, self -aspired learners reveal their I need to know and building skills that go beyond the classroom. It is not just about knowledge – but about the preparation of students to adapt, grow and innovation in the ever -changing world.
Additional resources:
The four stages of the self -taught training model
Student Teacher
Stage 1 Dependent authority, coach
Examples: Coaching with immediate feedback. Workout. Information lecture. Overcoming flaws and resistance.
Stage 2: Interested motivator, guide
Examples: Inspirational lecture plus a guided discussion. Strategies for setting goals and training.
Stage 3: Participating facilitator
Examples: Discussion facilitated by the teacher who participates as equal. Seminar. Group projects.
Stage 4: Independent consultant, delegator
Examples: internship, dissertation, individual work or self -directed learning group.
Teaching and Training Theories: The gradual self -assembled training model, G.Grow. from Barbara Stokes; Four stages of self -targeted training model

