2000-2003
Digital instruments begin to enter the classrooms, led by interactive white boards and early online platforms such as Blackboard. The basics are laid from analog to the methods of digital teaching.
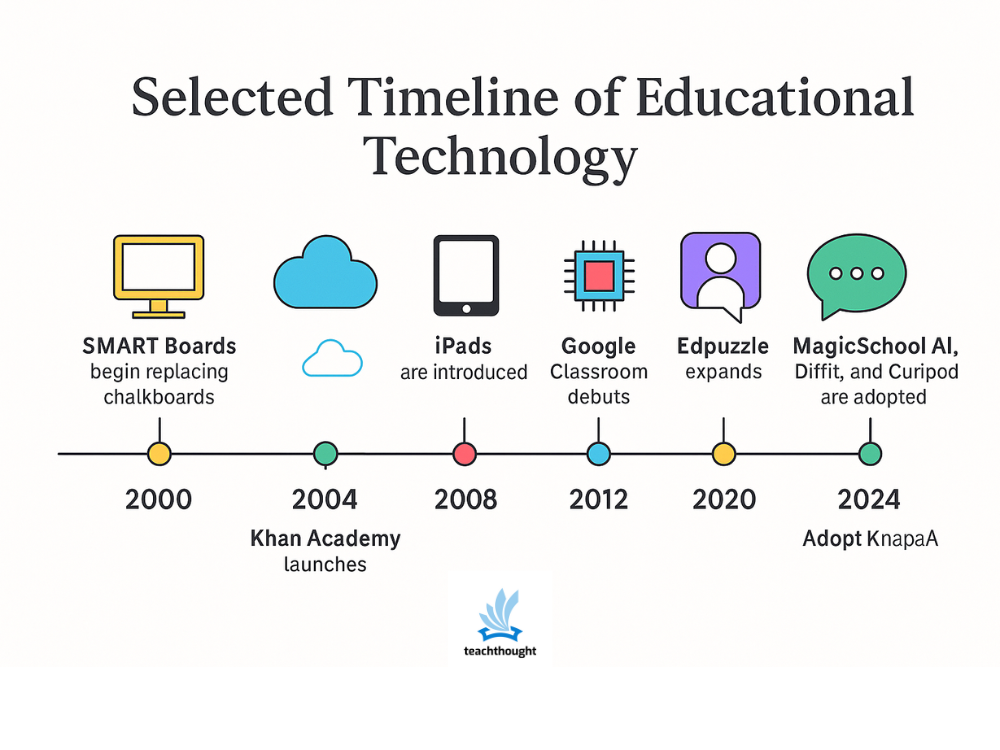
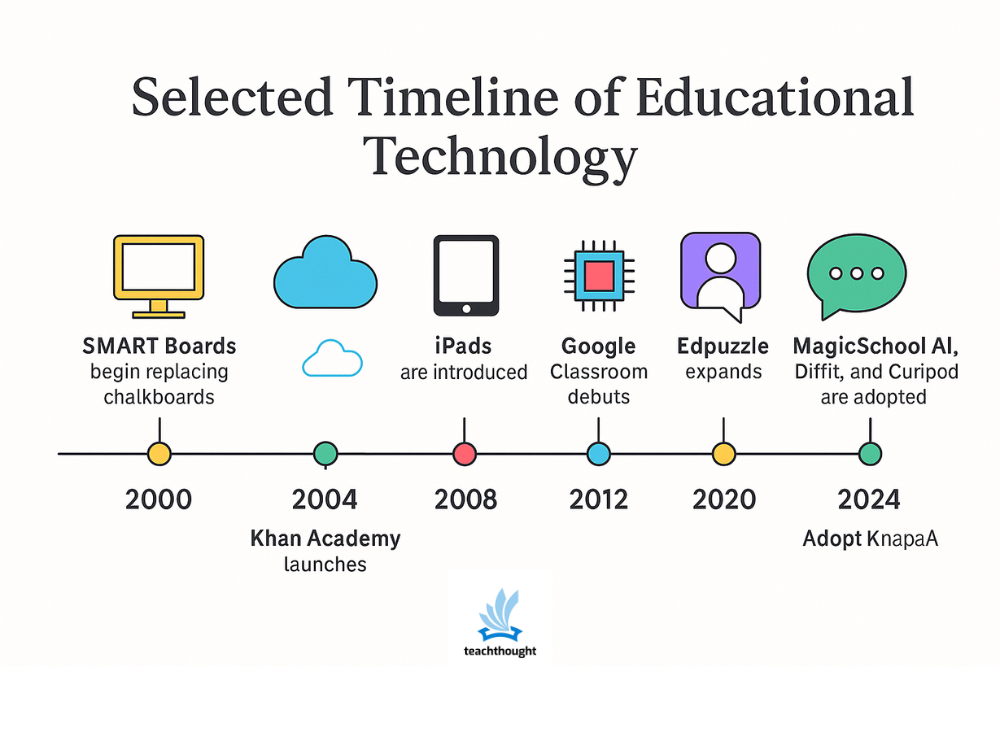
- Smart boards are beginning to replace the boards in the United States, offering early digital interactivity.
- The bladka is expanding In higher education, centralization of curricula, tasks and grades.
- BrainPop and Discovery Education Start Subscription Based Video and K-12 Lessons.
- Microsoft PowerPoint is becoming a major for teachers and projects for students.
2004–2007
Open -code cloud tools and platforms are speeding. YouTube and Google Docs note a turning point in cooperation and access to content.
- YouTube launches And it began its evolution at the main center for educational video content.
- Moodle emerges as an open source LMS, which allows for the delivery of courses and tracking students.
- Google Docs presents a browser -based cooperation in real -time task writing.
- Maine Training Technology Initiative is expanding national laptop programs one to one.
2008–2011
The rise of mobile devices – especially the iPad – is to reshape how the more young learners have access to digital content. The Khan Academy sets a precedent for free, upon request, on request.
- Han Academy Starts With short mathematics lessons, becoming a leader in free video based instructions.
- The iPad is introduced in 2010 and quickly integrates into K -2 classrooms for literacy and accessibility.
- Document cameras replace the above -ground projectors, which allows dynamic display and annotation of print content.
2012–2015
Google’s educational ecosystem is shaped by launching the classroom and wide admission of Chromebook. These years set the standard of delivery of training in the cloud.
- Google’s classroom debuted in 2014, simplifying the distribution and collection of digital tasks.
- Chromebooks sell iPad In education in the United States for the first time, driven by costs and cloud integration.
- Beauspod and Pear Peck introduce interactive, devices -based engagement with slides and surveys.
2016–2019
Student voice instruments, interactive videos and formats based on inquiries are gaining popularity. This period focuses on creating and engaging more than access to content.
- FlipGrid allows asynchronous responses to videos, becoming popular in classrooms worldwide.
- Edpuzzle expands The use of built -in video questions for a formal evaluation.
- Adobe Spark (now Adobe Express) is becoming a choice tool for projects designed for students, tasks, etc.
- Hyperdocs are emerged as developed by Google Docs for inquiries based.
2020–2023
The Covid-19 pandemic pandemic accelerates the full-scale intake of digital instructions. Teachers are embracing (because what choice most do?) Asynchronous instruments and AI enter into the educational conversation.
- Distance training during the Covid-19 pandemic drives the mass admission of Zoom, Google Meet and teams.
- Teachers use shielding and getting up to record asynchronous lessons and explanations.
- Khango starts Like the GPT-4-GP-4-Nourishing AI teacher and assistant to Academy.
- Wakelet, Padlet and Jamboard (who has been from sunset since then) has become popular for curating, brainstorming and visual collaboration.
2024–2025
AI tools are beginning to convert instruction design, feedback and policy. Teachers adapt to a new era of automation, ethical dilemmas and content generation.
- Teachers accept Magicschool AI., DifferentAnd Curipod for skeletal texts, distinguishing tasks and fast construction of materials.
- The areas are implementing policies to use generative AI, focusing on academic integrity and authorship.
- Professional development is shifting to emphasize rapid engineering, leveling of AI and instructional ethics.
- Teachers re -produce assessments of synthesis priority, real -world application and multimodal expression.